Subtotal ₹0.00
Eczema Symptoms: Causes and Effective Treatments
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by red, inflamed, and itchy skin. It can affect people of all ages but is most commonly seen in infants and young children. For many, it is a long-term condition, with periods of flare-ups followed by remission. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of eczema is essential for managing it effectively and improving quality of life.
Symptoms of Eczema
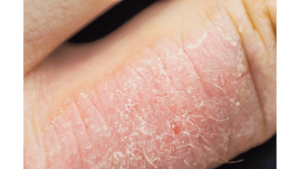
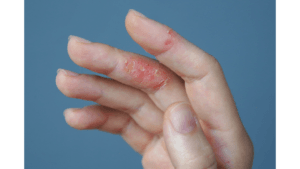
The hallmark symptom of eczema is itchy skin, which can become unbearable at times, leading to scratching that worsens the condition. Eczema symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the condition, but common symptoms include:
- Dry, sensitive skin: Skin may become very dry, making it prone to cracking and irritation.
- Itching: Persistent itching is a defining feature, often worsening at night or in dry conditions.
- Red or brownish-gray patches: These can appear anywhere on the body but are common on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, and the bend of the elbows and knees.
- Thickened, leathery skin: Prolonged scratching can cause the skin to thicken in affected areas, leading to a leathery texture known as lichenification.
- Small, raised bumps: These may ooze fluid when scratched and can scab over.
- Crusting or scaling: Affected areas may develop crusts or flakes due to dryness or infection.
- Swelling or sensitivity: Eczema can make skin areas highly sensitive and prone to swelling when irritated.
While these are the primary symptoms, eczema can be more complex, with some individuals experiencing secondary infections due to skin damage caused by scratching.
Causes of Eczema
The exact cause of eczema remains unclear, but research suggests it arises from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with eczema often have a weakened skin barrier, making it more difficult to retain moisture and protect against irritants, allergens, and bacteria. Here are some of the leading causes and triggers:
- Genetic predisposition: Eczema tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component. A defective gene responsible for producing filaggrin, a protein that helps maintain the skin’s barrier, has been linked to eczema. People with a family history of eczema, hay fever, or asthma are more likely to develop the condition.
- Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors can trigger eczema flare-ups. These include exposure to irritants such as soaps, detergents, and perfumes, as well as allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. Extreme weather conditions, including very dry or humid climates, can also exacerbate symptoms.
- Immune system dysfunction: Eczema is thought to be an immune-related condition, where the immune system overreacts to irritants or allergens, causing inflammation in the skin.
- Stress: Emotional stress can trigger or worsen eczema symptoms in many individuals. Though it does not directly cause eczema, stress can activate the immune system, leading to flare-ups.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially in women, can trigger or worsen eczema. For instance, eczema may flare up during pregnancy or just before menstruation.
- Food allergies: In some individuals, certain foods can trigger eczema, especially in infants and children. Common food triggers include dairy products, eggs, soy, wheat, and nuts.
- Sweat and heat: Sweating and overheating can worsen the itchiness and irritation associated with eczema, making physical activity or exposure to hot environments a trigger for some individuals.
Effective Treatments for Eczema
Although there is no cure for eczema, various treatments can help manage symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and prevent the condition from worsening. The goal of treatment is to restore the skin’s barrier, control inflammation, and relieve itching.
1. Moisturizing and Skin Care
Keeping the skin moisturized is the cornerstone of eczema management. Since people with eczema have a compromised skin barrier, frequent application of moisturizers helps lock in moisture, reduce dryness, and provide a protective layer. Here are some key tips:
- Emollients: Use thick, fragrance-free moisturizers or ointments such as petroleum jelly or mineral oil. These should be applied immediately after bathing to seal in moisture.
- Regular baths: Short, lukewarm baths or showers help hydrate the skin. Avoid hot water, which can strip the skin of natural oils. Using gentle, soap-free cleansers is crucial to prevent further irritation.
- Humidifiers: Using a humidifier in dry environments can help keep the air moist and prevent eczema from flaring up during colder months.
2. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching:
- Topical corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory creams and ointments are commonly prescribed for eczema flare-ups. They reduce redness, swelling, and itching. However, long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to side effects such as thinning of the skin.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: These non-steroidal medications, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, suppress the immune system’s response, helping to reduce inflammation and itching without the side effects associated with corticosteroids.
- Barrier repair creams: These creams help restore the skin’s natural barrier by replenishing the lipids that are often deficient in eczema patients. Products containing ceramides are particularly effective.
3. Oral Medications
In severe cases, where topical treatments are not sufficient, doctors may prescribe oral medications:
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines can help relieve itching, especially if it disrupts sleep.
- Oral corticosteroids: These are sometimes prescribed for short-term use during severe flare-ups. They are effective in reducing inflammation but can have significant side effects if used long-term.
- Immunosuppressants: Drugs like cyclosporine or methotrexate may be used in severe cases to suppress the immune system and prevent flare-ups. However, they are typically reserved for people who have not responded to other treatments.
4. Light Therapy (Phototherapy)
For people with moderate to severe eczema, light therapy can be an effective treatment option. It involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural sunlight or ultraviolet (UV) light. Phototherapy can reduce inflammation, improve the skin barrier, and alleviate itching. However, it requires regular sessions and must be performed under medical supervision to minimize the risk of skin damage.
5. Biological Treatments
Newer treatments, such as biologics, have emerged for severe eczema cases. Biologics target specific components of the immune system that contribute to inflammation. Dupilumab (Dupixent) is one such biologic approved for treating moderate to severe eczema. It is administered by injection and has shown promising results in reducing symptoms.
6. Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
- Identify and avoid triggers: Identifying triggers, such as specific foods, fabrics, or environmental conditions, and avoiding them can prevent flare-ups.
- Stress management: Since stress is a known trigger, adopting relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help manage flare-ups.
- Cold compresses: Applying a cold compress to itchy areas can provide temporary relief without scratching, which can further damage the skin.
Homeopathic Treatment of Eczema
Homeopathy offers a natural and holistic approach to treating eczema, focusing on stimulating the body’s self-healing abilities. The treatment is individualized, meaning remedies are selected based on a person’s specific symptoms, overall health, and emotional state. Common homeopathic remedies for eczema include:
- Graphites: Useful for dry, rough skin with thickened patches and cracks.
- Sulphur: Often prescribed for intensely itchy, burning skin, especially when aggravated by heat.
- Rhus Toxicodendron: For eczema with intense itching and blistering, often worsened by cold and improved by warmth.
- Mezereum: Beneficial for eczema with thick crusts and oozing, especially on the scalp.
- Arsenicum Album: For dry, scaly eczema with burning sensations that worsen at night.
In homeopathy, remedies are chosen according to the individual’s overall constitution and symptoms. Patience and consistency are key, as results may take time, and it’s always advised to consult a certified homeopath for a personalized treatment plan. Book your appointment for Eczema Treatment with PDM Homeopathy Hospital.
Conclusion
Eczema is a complex, multifactorial condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the causes and symptoms is essential for effective management. While there is no cure, a combination of moisturization, topical treatments, lifestyle changes, and, in severe cases, advanced medical treatments can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with eczema. Managing triggers and keeping the skin well-hydrated are key strategies to control flare-ups and reduce discomfort.